The Legacy of Old Mexican Mining Ovens: Preserving a Crucial Piece of Mining History
Introduction
Mexico’s diverse landscapes are celebrated for their rich cultural heritage and stunning natural beauty, but they also hold a lesser-known yet crucial chapter in the history of mining. Central to this story are the traditional Mexican mining old mexican mining ovens ovens, or “hornos de cal,” which played an essential role in the country’s mining industry, especially during the colonial and early post-colonial eras. These historic ovens were more than just tools of the trade; they were vital to the economic and social development of Mexico. This article explores the history, architecture, and cultural significance of these old mining ovens, shedding light on their impact and enduring legacy in shaping Mexico’s mining heritage.
The Evolution of Mining in Mexico
Mining has deep roots in Mexico, stretching back to pre-Columbian civilizations such as the Aztecs and Maya, who were skilled in extracting a range of minerals. However, it was during the Spanish colonial era that Mexican mining old mexican mining ovens saw a dramatic expansion. The Spanish conquest in the early 16th century introduced advanced mining technologies and an intense quest for precious metals. This led to the discovery of extensive silver deposits in regions like Zacatecas and Guanajuato, propelling Mexico to the forefront of global silver production and reshaping its economic landscape.
The Emergence of Mexican Mining Ovens
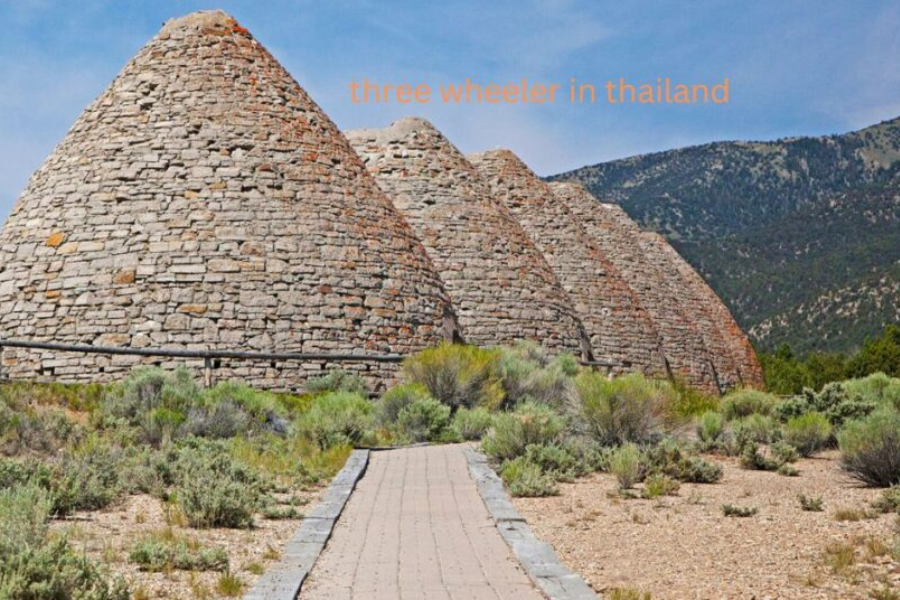
As Mexico’s mining industry expanded, there arose a need for more efficient methods to process ore. Enter the “hornos de cal,” or Mexican mining ovens, which became crucial in turning raw ore into usable materials. These old mexican mining ovens ovens were primarily used to produce quicklime, an essential component in the smelting process. Quicklime, or calcium oxide, was created by heating limestone to high temperatures in these ovens, breaking it down into lime and carbon dioxide.
Architectural Characteristics
Design and Construction
Mexican mining ovens are distinguished by their unique architectural features. Typically built from local materials such as stone or adobe, old mexican mining ovens these ovens were designed to endure the intense heat required for lime production. The design of these ovens often adapted to local geological conditions and the materials at hand.
A typical mining oven consists of several key components:
- Chimney: A tall, narrow chimney facilitated the expulsion of gases and smoke produced during the lime-burning process.
- Kiln Chamber: The central chamber where limestone was placed and heated. This chamber was usually cylindrical or old mexican mining ovens dome-shaped to ensure uniform heating.
- Firebox: Positioned at the base of the oven, the firebox was where fuel, typically wood or charcoal, was burned to generate the necessary heat.
- Drafts and Vents: These features allowed for proper air circulation and temperature control within the oven.
Regional Variations
The design of mining ovens varied across Mexico, reflecting the local resources and mining practices. In some regions, ovens were built into hillsides or natural rock formations to improve insulation and heat retention. In other old mexican mining ovens areas, more elaborate structures were constructed to meet the needs of larger mining operations.
The Impact of Mining Ovens on Mexico’s Industry and Culture
Lime Production
Mining ovens were integral to the extraction of valuable metals in Mexico’s colonial mining industry. Their primary role was to produce old mexican mining ovens quicklime, which was a key component in the smelting process. Quicklime acted as a flux, helping to separate impurities from the metal and enhancing the efficiency of the smelting process.
Economic Impact
The production of quicklime was essential to Mexico’s economic growth during the colonial era. The demand for lime was high, driven not old mexican mining ovens only by mining operations but also by construction and agriculture. The thriving mining industry significantly boosted Mexico’s economy, and the effective operation of these ovens was central to this success.
Labor and Community
Running these ovens was a demanding task that required skilled labor. Many of the workers were local indigenous people, who old mexican mining ovens often faced tough working conditions. The presence of mining ovens led to the establishment of mining communities around major sites, spurring the development of infrastructure and local economies.
Cultural and Historical Significance
Legacy of Mining Ovens
Old Mexican mining ovens are more than just historical artifacts; they are emblematic of Mexico’s rich mining heritage. Many of these structures have been preserved and are now celebrated as important cultural and historical landmarks. They offer valuable insights into the technological advancements and economic practices of the past.
Preservation and Tourism
Recent efforts have focused on preserving these historic ovens, with many being included in heritage sites and museums. These locations old mexican mining ovens provide visitors with a glimpse into Mexico’s mining history and educate the public about the significance of these structures and the labor force behind them.
Modern Relevance
Studying old Mexican mining ovens is not only about exploring the past but also about understanding their relevance to modern industries and historical research. The techniques used in these ovens offer lessons in traditional lime production methods, informing contemporary practices and deepening our understanding of historical mining technologies.
Preserving the Past: Challenges and Future Directions
Conservation Efforts
The preservation of old Mexican mining ovens is facing significant challenges. These historic structures are threatened by natural erosion, vandalism, and inadequate funding for maintenance. To protect these valuable remnants of Mexico’s mining heritage, a unified effort is needed from local communities, historians, and conservationists. Addressing these issues requires resources, awareness, and commitment to ensure that these ovens continue to tell their important stories.
Promoting Awareness
Raising awareness about the historical significance of these mining ovens is essential for their conservation. Educational programs, community engagement, and tourism initiatives can play a key role in emphasizing their value. By old mexican mining ovens highlighting their cultural and historical importance, we can foster a sense of appreciation and responsibility toward preserving these unique structures for future generations.
Research and Documentation
Continued research and documentation are vital for deepening our understanding of old Mexican mining ovens. Archaeological investigations, historical research, and oral histories offer valuable insights into their technological and historical significance. These efforts help paint a fuller picture of the role these ovens played in Mexico’s mining industry and contribute to our broader knowledge of historical mining practices.
FAQs:
1. What were old Mexican mining ovens used for?
Old Mexican mining ovens, known as “hornos de cal,” were primarily used for producing quicklime. Quicklime was a crucial ingredient in the smelting process, helping to separate impurities from ore and improve the efficiency of metal extraction.
2. What materials were used to construct these ovens?
These ovens were typically constructed from local materials such as stone or adobe. Their design was adapted to withstand the high temperatures required for lime production.
3. How did old Mexican mining ovens impact the economy?
The production of quicklime was essential for the mining industry and had a significant economic impact. Lime was in high demand not only for mining but also for construction and agriculture, contributing to Mexico’s economic growth during the colonial period.
4. What are the main challenges in preserving old Mexican mining ovens?
Challenges include natural erosion, vandalism, and insufficient funding for maintenance. Conservation efforts require collaboration among local communities, historians, and conservationists to ensure these structures are preserved.
5. How can the public contribute to the preservation of these historical sites?
Public awareness and engagement are crucial. Educational programs, community involvement, and responsible tourism can help highlight the importance of preserving old Mexican mining ovens and support conservation initiatives.
Conclusion
Old Mexican mining ovens are a significant part of Mexico’s industrial heritage, representing a critical aspect of the country’s mining history. These structures played a vital role in the production of quicklime, which was essential for smelting processes and economic development during the colonial era. Their unique architectural features and historical impact make them valuable cultural landmarks.
However, preserving these ovens poses several challenges, including natural degradation and vandalism. To ensure their survival for future generations, it is essential to promote awareness, engage in conservation efforts, and support research and documentation. By doing so, we can honor the legacy of these historical structures and continue to learn from their rich history and technological advancements.
Explore intriguing articles and the newest trends in entertainment at Tamasha.blog.